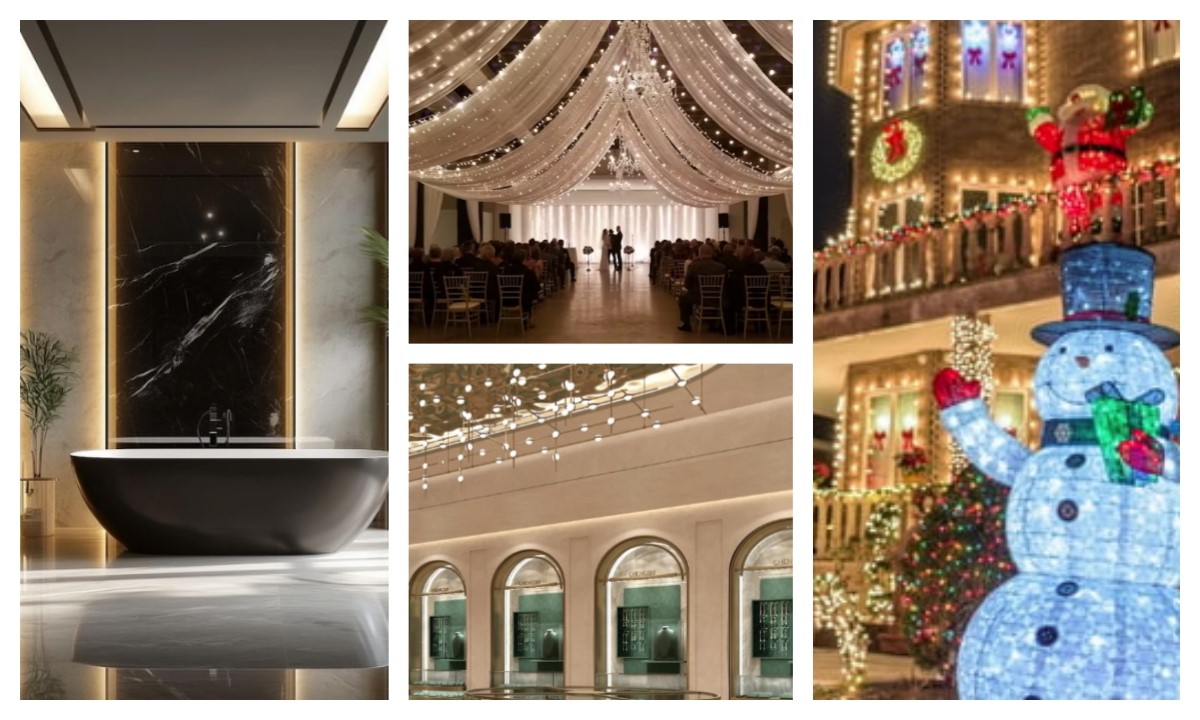
Table of Content
- 1. Apa itu Lampu Strip LED COB?
- 2. Apa itu Lampu Strip LED SMD?
- 3. Apa Perbandingan Teknis antara Strip LED COB dan Strip LED SMD?
- 4. Apa keuntungan dan kerugian strip LED COB?
- 5. Apa keuntungan dan kerugian strip LED SMD?
- 6. Apa saja perbandingan skenario aplikasi strip LED COB dan strip LED SMD?
- 7. Kapan Memilih Strip LED COB/Strip LED SMD?
- 8. Apa perbedaan antara Strip LED COB dan Strip LED SMD dalam hal penyambungan/pemasangan/penyalaan?
- 9. Tanya Jawab Umum tentang Strip LED COB/Strip LED SMD
- 10. Ringkasan
COB led strips and SMD led strips are commonly utilized in modern life. But how much do you really know about them?
In this guide, I will show you elaborate knowledge of COB led strips and SMD led strips, including their definitions, features, technical/connecting/powering/installation comparisons, pros and cons, applications, when to use, and common problems.
1. What is COB Led Strip Light
(1) Definition
COB (Chip On Board) LED Strip refers to a type of LED lighting technology utilizing Chip-on-Board (COB) manufacturing processes. It involves placing LED chips directly onto a circuit board, bypassing the need for individual lamp beads, creating a seamless, high-density arrangement of light-emitting units.
(2) Features
Simplified Structure: Replaces traditional packaging processes, making it simpler and lower costs.
Enhanced Brightness and Contrast: Achieves higher luminance and contrast ratios compared to conventional LEDs.
Energy Efficiency: Costs lower power consumption for less energy loss and optimized thermal management.
Durability: The compact design minimizes the risk of damage from external factors like moisture.
2. What is SMD Led Strip Light
2.1 Definition
SMD stands for Surface-Mounted Device, referring to LED chips directly soldered onto a flexible printed circuit board (PCB).
2.2 Features
(1) Design and Structure:
Individual Diodes: Each LED is a separate unit soldered onto the PCB.
Modular Layout: Diodes are spaced evenly along the strip, creating visible light points.
Flexible PCB: Allows bending and cutting (at marked intervals) for custom installations.
(2) Light Quality:
Beam Angle: Typically 120°.
Brightness: Higher lumen output per watt.
Color Options: Available in single color or RGB/RGBW for dynamic lighting.
(3) Energy Efficiency:
Optimized for high brightness with lower power consumption.
3. What are the Technical Comparisons between COB Led Strip and SMD Led Strip?
(1) Structure:
COB Led strip: Uses Chip-on-Board technology, embedding LED chips directly onto the substrate.
PCB+LED Chips+Silicone phosphor+epoxy/silicone(If it is waterproof)
SMD Led strip: Feature individual surface-mounted diodes with visible light points.
PCB+SMD LEDs+epoxy/silicone(If it is waterproof)
(2) Optical Performance
| Parameter | COB LED Strips | SMD LED Strips |
| Luminous Efficacy | 120–150 lm/W (high-power COB up to 200 lm/W) |
80–120 lm/W (standard 5050 SMD) |
| Brightness Uniformity | Single-chip design minimizes hotspots (±5%) |
Multiple SMDs may create visible brightness variations (±15%) |
| Color Consistency | Integrated phosphor coating ensures tight binning |
Discrete SMDs require strict binning for uniformity |
(3) Thermal Management
COB Led Strip:
Generate concentrated heat due to densely packed chips and use low thermal resistance materials (chip-to-aluminum substrate) for effective dissipation.
SMD Led Strip:
Spread heat across a larger PCB area, reducing localized overheating. Require additional simpler heat sinks.
(4) Flexibility Design
COB Led Strips:
Ultra-thin, flexible design (no bulky diodes) for seamless integration into tight spaces.
No exposed gold wires, reducing the risk of corrosion or damage.
SMD Led Strips:
Thicker profile due to individual diodes but offers customizable color temperatures and RGB options.
Easier to cut and reconfigure at marked intervals.
(5) Lifespan & Reliability
COB Led Strip:
Longer lifespan (up to 50,000 hours) with slower light degradation.
Less prone to solder joint failures due to fewer components.
SMD Led Strips:
An average lifespan of 50,000 hours (dependent on chip quality).
Higher risk of single-LED failure in dense configurations.
(6) Cost
COB Led Strip:
Higher upfront cost (complex manufacturing) but lower long-term maintenance.
Lower maintenance costs due to fewer failure points.
SMD Led Strips:
Cost-effective for short runs and temporary installations.
Potential long-term expenses from LED replacements.
| Summary Table | ||
| Feature | COB LED Strips | SMD LED Strips |
| Structure | Use Chip-on-Board technology, embedding LED chips directly onto the substrate. | Feature individual surface-mounted diodes with visible light points. |
| Light Uniformity | Dotless, seamless beam | Visible light points |
| Beam Angle | 180° | 120° |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower power consumption | Higher lumen/watt efficiency |
| Durability | Longer lifespan, better heat management | Moderate lifespan, simpler cooling |
| Flexibility Design | Ultra-thin, ideal for tight spaces | Thicker, but easier to cut/reconfigure |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Budget-friendly |
4. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of COB Led Strips?
4.1 Advantages:
(1) Superior Light Uniformity
Monolithic chip design eliminates visible light points.
180° diffusion minimizes shadows.
(2) High Brightness and Energy Efficiency
COB strips achieve high lumen output with lower power consumption due to reduced energy loss in the integrated design.
(3) Durability and Longevity
Extended Lifespan: With lifespans of 50,000+ hours, COB strips outlast many SMD alternatives.
Fewer Failure Points: Reduced solder joints lower the risk of single-component failure.
(4) Space-Saving Design
Ultra-Thin and highly flexible Profile: 1.6mm rigid PCB allows flush mounting in confined spaces. And allows installation in tight spaces like curved surfaces or corners.
No Exposed Components: Gold wires are embedded, preventing corrosion in harsh environments.
(5)Wide Voltage Compatibility
Most COB strips support 5V, 12V, or 24V power inputs.
4.2 Disadvantages:
(1) Higher Upfront Cost
COB strips are pricier due to complex manufacturing.
(2) Heat Concentration
Poor thermal management can shorten lifespan.
(3) Limited Customization
Fixed color temperatures and configurations limit design flexibility (e.g., warm white, cool white).
(4) Fragility During Installation
Thin, flexible designs can be easily damaged during handling.
(5) Repair Challenges
Damaged sections are harder to repair compared to SMD strips, as COB’s integrated design makes individual LED replacements impractical.
5. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of SMD Led Strips?
5.1 Advantages:
(1) Cost-Effective
SMD strips are cheaper to produce and purchase.
Simplified manufacturing reduces component costs.
(2) Wide Range of Color Options
Adjustable LED spacing and RGB/RGBW color options.
Bendable up to 5mm radius, ideal for curved surfaces or confined spaces.
(3) Repairability
Modular Replacement: A single SMD LED can be desoldered and replaced.
Easy Cutting: Pre-marked segments allow quick length adjustment without damaging the circuit.
(4) High Brightness with Good Efficiency
SMD LED strips achieve high lumen output with decent energy efficiency.
(5) Simplified Heat Dissipation
Heat spreads across the wider PCB surface, reducing the risk of localized overheating. Works well with basic aluminum channels or heat sinks.
(6) Diverse Applications
Versatile Lighting: Common in home decor, automotive lighting, and signage.
High Color Rendering: CRI≥90 options available for accurate color representation.
5.2 Disadvantages:
(1) Visible Light Dots and Hotspots
Individual LEDs create uneven light distribution, especially in reflective environments.
(2) Shorter Lifespan
Typically it lasts approximately 45,000–50,000 hours. Prolonged high-temperature use accelerates degradation.
(3) Narrower Beam Angle
A standard 120° beam angle limits coverage, requiring more strips for wide-area illumination.
(4) Less Durable in Harsh Conditions
Exposed diodes and solder points make them prone to damage from moisture, dust, or physical impacts unless properly sealed.
(5) Complex Repairs and Higher Maintenance
Fixing a faulty section often requires soldering skills, and mismatched batches can cause color/temperature inconsistencies.
One defective SMD may require replacing the entire segment.
Double-sided tape loses adhesion faster in high-temperature settings.
(6) Power Limitations
Lower Brightness: Maximum 170 lm/W (standard 80–120 lm/W), unsuitable for high-lux environments.
Voltage Drop Risks: Long runs may require additional power injection to prevent voltage drop and dimming at the strip’s end.
6. What are the Comparisons between COB Led Strip and SMD Led Strip Application Scenarios?
6.1 Residential Lighting
(1) COB LED Strips
Best For:
Seamless Ambient Lighting: Spots like stair accents where uniform, glare-free illumination is important.
High-End Decor: Modern interiors such as luxury bathrooms require a clean, dotless appearance.
Indirect Lighting: Behind TVs or mirrors for smooth backlighting without visible hotspots.
(2) SMD LED Strips
Best For:
Decorative Accents: Color-changing RGB strips for gaming setups, or holiday decorations.
Task Lighting: Under-cabinet lighting in workshops where brightness is prioritized over uniformity.
DIY Projects: Customized installations like bookshelves that can easily be cut and reconfigured.
6.2 Commercial and Retail Spaces
(1) COB LED Strips
Best For:
Premium Displays: Museum exhibits and jewelry cases requiring flawless, shadow-free lighting.
Architectural Highlighting: Accent lighting for curved surfaces, and columns with a seamless glow.
Hospitality: Hotels or restaurants aiming for a luxurious ambiance with hidden light sources.
(2) SMD LED Strips
Best For:
Cost-Effective Signage: Backlit signs or menu boards where visible light points are acceptable.
General Illumination: Warehouse or office task lighting with high brightness at a lower cost.
Event Lighting: Concerts or weddings using RGB strips for dynamic color effects.
6.3 Automotive and Transportation
(1) COB LED Strips
Best For:
Interior Mood Lighting: Car cabins or yachts where slim, durable strips with smooth light enhance aesthetics.
Exterior Accents: License plate lighting or underbody accents requiring weather-resistant, compact designs.
(2) SMD LED Strips
Custom Car Mods: Underglow lighting or DIY automotive projects using RGB strips for vibrant effects.
Trucks/Buses: Functional lighting like step lights where durability and affordability matter more than uniformity.
6.4 Outdoor and Industrial Use
(1) COB LED Strips
Best For:
Architectural Landscaping: Pathways or water features where waterproof, seamless lighting is needed.
Industrial Displays: High-precision environments like labs requires consistent, durable illumination.
(2) SMD LED Strips
Best For:
Outdoor Festivals: Temporary installations like Christmas lights, and party tents using waterproof RGB strips.
Workshops/Garages: Task lighting with high brightness and replaceable sections if damaged.
6.5 Specialized Applications
(1) COB LED Strips
Best For:
Medical Lighting: Surgical or diagnostic equipment needing flicker-free, high-CRI light.
Aviation/Transport: Aircraft cabin lighting with ultra-thin, vibration-resistant designs.
(2) SMD LED Strips
Best For:
Entertainment: Themed attractions such as escape rooms, and theaters using RGB for immersive effects.
Agriculture: Grow lights with tunable spectra for plant growth (using specialized SMD chips).
7. When to Choose COB Led Strips/SMD Led Strips?
7.1 Choose COB LED Strips When…
7.2 Choose SMD LED Strips When…
8. What are the Differences between COB Led Strips and SMD Led Strips When Connecting/Powering/Installing?
8.1 COB LED Strips
(1) Pre-Installation Preparation: Measure the Area, clean the Surface, and test the Strip.
(2) Cutting the COB LED Strip at Marked Intervals.
(3) Wiring and Connections
Option A: Soldering
Strip the wire ends (1–2mm).
Tin the tiny copper pads on the COB strip with solder.
Solder wires to the pads.
Cover joints with heat shrink tubing to insulate.
Option B: Solderless Connectors
Use COB-specific connectors for tool-free installation.
Slide the strip into the connector and clamp tightly.
(4) Mounting the Strip
Peel the adhesive backing and press the strip firmly onto the surface (For curved surfaces, use mounting clips instead of adhesive).
Install aluminum channels.
Secure channels with screws or adhesive.
(5) Powering the COB LED Strip
Use a constant-current driver to match the strip’s voltage and wattage.
Avoid daisy-chaining multiple strips—connect in parallel for long runs.
For waterproof installations (IP65/IP67).
(6) Testing
Turn on the power and check for uniform brightness and secure connections.
8.2 SMD LED strip
(1) Pre-Installation Preparation: Measure the Area, clean the Surface, and test the Strip
(2) Cutting the SMD LED Strip:
Cut at marked intervals (scissor icons).
Use sharp scissors for a clean cut through the copper pads.
(3) Wiring and Connections
Option A: Soldering
Strip the wire ends (1–2mm) and tin them with solder.
Tin the exposed copper pads on the SMD strip.
Solder wires to the pads, matching polarity.
Insulate connections with heat shrink tubing or electrical tape.
Option B: Solderless Connectors
Use snap-on connectors.
Open the connector, align the strip’s copper pads, and clamp it shut.
(4) Mounting the Strip
Peel the adhesive backing and press the strip firmly onto the surface (For curved surfaces, use mounting clips or flexible aluminum channels).
Use aluminum channels(optional)
Secure channels with screws or adhesive.
(5) Powering the SMD LED Strip
Use a constant-voltage driver.
Avoid voltage drop
For RGB/RGBW strips: Connect a controller between the power supply and the strip.
(6) Testing
Power on the strip and check for:
Consistent brightness.
Proper color output (for RGB models).
| COB vs SMD Installation Differences | ||
| Aspect | COB LED Strip | SMD LED Strip |
| Cutting Flexibility |
Limited to marked intervals (5–10 cm) |
Cut every 3 LEDs or 5 cm |
| Heat Management |
Mandatory aluminum channels | Optional aluminum channels for high-power |
| Wiring | Tiny pads, challenging soldering |
Larger solder pads, easier connections |
| Adhesive Strength |
Weak adhesive, often needs extra clips |
Strong 3M backing holds well |
| Voltage Drop |
Less prone due to integrated design |
Common in long runs (requires injection) |
9. COB Led Strips/SMD Led Strips FAQs
10. Summary
The LED lighting industry continues to evolve, driven by demands for energy efficiency, aesthetic versatility, and advanced performance. Market trends indicate parallel growth: COB adoption surges in high-brightness, precision-driven environments, while SMD retains its stronghold in volume-driven, decorative applications. Innovations in miniaturization and hybrid designs further blur traditional boundaries, suggesting a future where both technologies coexist, addressing divergent performance and budgetary requirements across global markets.