Table of Content
- 1. LED Strip Definition
- 2. LED Strip Core Components
- 3. LED Strip Types
- 3.1 Classification by Encapsulation Types
- 3.2 Classification by Protection Rating
- 3.3 Classification by Light Color
- 3.4 Classification by Bendability
- 3.5 Classification by Input Voltage
- 3.6 Classification by Driver and Voltage/Current Control Logic
- 3.7 Classification by SMD Led Size:
- 3.8 Classification by Direction of Light Emission:
- 3.9 Classification by Working Principle:
- 3.10 Classification by Cuttable Length:
- 4. LED Strip Features
- 5.Led Strip Cost Composition
- 6. LED Strip Quality Evaluation
- 7. How to Select the Right LED Strip
- 8. How to Power LED Strips
- 9. How to Connect LED Strip
- 10. LED Strip Installation & Maintenance
- 11. LED Strip Applications
- 12. LED Strip Best Manufacturers
- 13. LED Strip FAQs
- 14. Summary
LED strip lighting systems are widely recognized for their energy efficiency, extended operational lifespan, simplified installation, and environmental sustainability. These versatile solutions have become indispensable in applications ranging from architectural illumination and retail merchandising to automotive lighting.
In this guide, we will equip you with essential knowledge about LED strips, covering their definition, core components, operational principles, types, features, cost composition, quality evaluation, selection, powering, connect, installation, maintenance applications, best manufacturers, and advanced troubleshooting methodologies.
1. LED Strip Definition
An LED strip is a linear lighting module utilizing LED (Light-Emitting Diode) technology, consisting of multiple high-efficiency LED emitters arranged on flexible or rigid substrates to form a continuous, elongated structure.
1.1 LED Strip Technical Parameters
1.1.1 Photoelectric Parameters
(1) Luminous Flux: The total amount of light emitted by the lamp, with the unit of lumen (lm).
(2) Luminous Intensity: Refers to the amount of light emitted by a source in a particular direction, measured in candelas (cd). The prefix “milli-” (meaning one-thousandth) is used to express smaller values, resulting in millicandela (mcd).
(3) Color Temperature (CCT): Characterizes light chromaticity in Kelvin (K)(From 2200K-18000K):
Warm White: 2700-3500K (relaxed ambiance)
Natural White: 4000-5000K
Cool White: 5000-6500K (task-oriented environments)
Deep Cool White: 8000-12000K
(4) Color Rendering Index (CRI): Measures the ability of the light source to restore the true color of the object, with a value range of 0 – 100. Color Rendering Index (CRI) ≥80 (standard), ≥90 (high-CRI for retail/art), ≥97(Super high)
(5) Luminous Efficacy: Light output efficiency expressed as lumens per watt (lm/W), calculated by dividing total luminous flux by electrical power consumption.
(6) Wavelength Tolerance: ±3nm.
(7) Beam Angle: 30° (spotlight) to 270° (wide diffused).
(8) Brightness Control: PWM dimming (8-bit to 16-bit precision).
1.1.2 Electrical Parameters
(1) Input Voltage: Operational voltage requirements: 3V/5V/12V/24V/36V/48V DC (±10% tolerance)(low voltage input) or 110V/220VAC(high voltage input)
(2) Input Current: The magnitude of the current passing through the LED strip, with the unit of ampere (A) or milliampere (mA). The magnitude of the current is related to the power and voltage of the LED strip. The calculation formula is I=P/V (where I is the current, P is the power, and V is the voltage).
(3) Power: Ranges from 2-46W/m depending on LED density and input voltage and input current configuration.
(4) Max Current per Segment: 0.2–6A (limited by PCB trace width and copper weight).
1.1.3 Mechanical & Structural Parameters
(1) PCB Type:
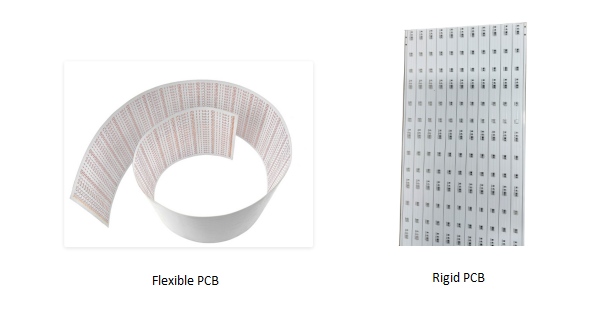
Flexible (FPC): Polyimide, bend radius >30mm.
Rigid (FR4): 0.6–1.6mm thickness.
Metal-core (MCPCB): An aluminum substrate for thermal management.
(2) LED Density: LED strip density refers to the number of LED chips per meter (LEDs/m), a important parameter influencing brightness, light uniformity, energy consumption, and cost.
(3) Strip Width: LED strip width refers to the physical width of the printed circuit board (PCB) on which the LEDs are mounted, measured in millimeters (MM).
(4) Cuttable Length: The cuttable length of LED strips is determined by segment intervals and total length limitations, which depend on strip type, voltage specifications, and application scenarios.
(5) Bending Radius: The minimum radius at which the LED strip can be bent without damage, with the unit of millimeter (mm). The smaller the bending radius, the better the flexibility of the LED strip.
(6) Ingress Protection Rating (IP): Represents the dust – proof and waterproof ability of the lamp, consisting of two digits. The first digit represents the dust – proof level (0 – 6), and the second digit represents the waterproof level (0 – 8). For example: IP54 or IP65 or IP67 or IP68 (The highest IP).
1.1.4 Power & Signal Integrity
(1) Voltage Drop parameters:
The voltage drop parameter of 24V is better than the 12V.If the input voltage of led strip is 24V,you can connect 10m or more in series.But if the input voltage is 12V,we suggest you connect 5m in series.
(2) Inner Copper Design:
Thickness: 1–2 oz/ft².
Width: 0.2–0.5mm (if thicker and wider,the resistance is smaller and Heat dissipation is better).
2. LED Strip Core Components
2.1 Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Component
Structure: LED chip+Bracket+Gold Thread+Phosphor
2.2 Substrate Material
Flexible PCBs: Polyimide FPC with bend radius ≥30mm
Rigid PCB: Aluminum PCB or FR4 PCB
Advanced Materials: Ceramic substrates for high-power applications
2.3 Electronic Components
Resistor, capacitor, transistors, LED driver IC and so on.
2.4 Optical Components
Lens component and Phosphor coatings for white light generation (2700K-6500K CCT)(for COB led strip)(Specialized phosphor coatings can achieve CRI>95)
2.5 Other Materials
Protective Coating: Silicone encapsulation or tube case(IP54/IP65/IP67/IP68 rated)
Adhesive: 300LSE or 200MP or …3M Adhesive Tape
Mounting Brackets: Aluminum Bracket or Plastic Bracket
Output wires: 2 pin wire(for single color strip) or 3 Pins wire(for CCT color strip) or 4 Pins wire(for RGB strip) or 5 Pins wire(for RGBW strip)
2.6 LED Strip Accessories
Connectors:direct connector or L shape connector or T shape connector or + shape connector…
Cabling: AWG stranded wire with 0.5mm² or 0.75mm² or 1.0mm² cross-section
Adapter(LED power supply): change input voltage from 110VAC or 220VAC or 230VAC to DC12V or DC24V or DC36 or DC48V for low input voltage led strips
3. LED Strip Types
3.1 Classification by Encapsulation Types
(1) Surface Mounted Device (SMD) Encapsulation:
Technology: LEDs are soldered directly onto the PCB surface using reflow welding.
Structure: PCB+SMD LEDs+epoxy or silicone(If it is wateproof)
Advantages: Super Bright if using high bright SMD leds
IP Rating: Typically IP20 (unprotected) to IP54 or IP65 or IP67 or IP68
(2) Chip-on-Board (COB) Encapsulation:
Technology: Multiple LED chips integrated onto a single PCB substrate.
Structure: PCB+LED Chips+Silicone phosphor+epoxy or silicone(If it is wateproof)
Advantages:
Uniform high-luminance output
Better thermal management
Elimination of individual LED spacing
IP Rating: Typically IP20 (unprotected) to IP54 or IP65 or IP67 or IP68
(3) Chip-Scale Package (CSP) Encapsulation:
Technical Advantages:
Higher power density compared to traditional SMD
Better thermal management through direct heat dissipation
Improved reliability in high-bending applications
Cost-effective for mass production via automated pick-and-place processes
Features: Chip-scale packaging (thickness <0.5mm) on transparent PET/PC substrates
3.2 Classification by Protection Rating
(1) Non-Waterproof LED Strips (IP20/IP33)
Structure:
Exposed PCB or coated with conformal protective lacquer.
Protection:
IP20: Protection against solid objects ≥12.5mm (e.g., fingers), no water resistance.
IP33: Protection against spray water (60° angle from any direction).
Use Cases:
Dry indoor environments (e.g., closet lighting, TV backlighting).
(2) Drip-Proof LED Strips (IP54/IP65)
Process:
Thin epoxy/silicone coating (0.3–0.5mm thickness).
Protection:
IP54: Limited dust ingress + splash resistance (water from any direction).
IP65: Dust-tight + protection against low-pressure water jets (nozzle from any angle).
Limitations:
Splash-resistant but not submersible (e.g., bathroom mirror lighting).
(3) Fully Potted LED Strips (IP67/IP68)
Process:
Thick silicone potting (>1mm) with molded waterproof connectors.
Protection:
IP67: Dustproof + temporary submersion (1m depth, 30 minutes).
IP68: Dustproof + prolonged underwater immersion (customizable to 1–3m depth for 1–24 hours).
Testing:
Submersion up to 1m for 30 minutes (IEC 60529 compliant).
Applications: Outdoor landscape lighting, underwater fixtures (pools, fountains), and humid industrial environments.
(4) Silicone Extrusion LED Strips (IP67/IP68)
Process:
High-temperature molten silicone is extruded through a mold to form continuous, uniform encapsulation layers that protect LED chips and circuits.
Structure:
Inner Layer: LED board (flexible PCB or metal-core substrate) with LED chips.
Outer Layer: Seamless silicone jacket that fully encapsulates circuits and solder joints.
Features:
Extreme Environmental Resistance, Superior Mechanical Performance, and Optical Customization.
Applications: Underwater Scenarios etc.
3.3 Classification by Light Color
(1) Single color LED Strips
Features: emits a single, unchanging light color(warm white/cool white/red/green/blue).
Advantages: They come at a low cost, have a simple structure, and offer high stability.
(2) CCT Adjustable LED Strips
Features: Warm White+Cool White color led on one single led strip;Continuously adjusted within a range (from 2700K to 6500K). This adjustment can be done seamlessly using a controller or smart devices.
Advantages: They can adapt to different environmental needs and support smart combined with systems like Mi Home and HomeKit.
(3) RGB LED Strips
Features: By combining the three primary colors of red, green, and blue, these strips can produce over 16 million colors through a controller.
Advantages: They offer a wide range of colors and support dynamic effects.
(4) RGBW LED Strips
Features: In addition to the RGB colors, these strips include a white chip. This allows for the production of purer white light and more saturated colors.
Application Scenarios: Used in high – end commercial spaces, stage performances, and smart homes, provided the control system is compatible.
Advantages: The white light has a high color rendering index (CRI > 80 or CRI > 90), and the color transitions are more natural.
(5) RGBCCT LED Strips
Features: A multifunctional lighting solution combining RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color control with tunable white light (CCT, Correlated Color Temperature).
Advantages: Multifunctionality, Circadian Lighting, and High Color Accuracy.
(6) Special Color LED Strips
UV LED Strips: These are used for disinfection, currency verification, or creating fluorescent effects, for example, in escape rooms.
IR LED Strips: Employed in security monitoring and night photography as they emit invisible light.
3.4 Classification by Bendability
(1) Standard LED Strips: Designed with flexible PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) or Rigid PCBs.
(2) Bendable LED Strips
Flexible Substrate Technology:
Utilizes S shape flexible PCB (Printed Circuit Board) to allow controlled bending within a certain range
Applications: Residential Decoration, Commercial Spaces, Industrial & Automotive and Creative Design.
Advantages: Space Adaptability, Space-Saving, and Creative Decoration.
3.5 Classification by Input Voltage
(1) High-Voltage LED Strips
Definition:
Directly connected to high-voltage mains (110V/220V)
Features:
Driving Method: Uses integrated constant voltage/current drivers
Installation Convenience: Simplifies wiring by eliminating the need for external power adapters.
Applications: Residential lighting, Commercial venues, and Projects requiring streamlined cabling.
(2) Low-Voltage LED Strips
Definition: Input voltage is DC12V or DC24V or DC36V
Requires an external power supply (adapter) for voltage reduction from 110VAC or 220VAC to DC12V or DC24V or DC36V
Features:
Driving Method: Relies on dedicated power adapters for safe low-voltage operation.
Safety: Operates at ≤36V, ideal for areas with frequent human contact (furniture, children’s rooms).
Applications: Safety-critical environments, Long-distance installations or expandable systems, and Precise dimming scenarios.
3.6 Classification by Driver and Voltage/Current Control Logic
(1) Constant Voltage LED Strips
Definition: A Constant Voltage (CV) LED Strip is a lighting product designed to operate at a fixed input voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V DC), with current varying dynamically based on the strip’s electrical load.
Features:
Voltage Range: Strictly matched to the power supply.
LED Configuration: Typically 3 LEDs(DC12V) or 6 LEDs(DC24V) in series per segment, creating voltage-dividing circuits.
Dimming Compatibility: Supports PWM dimming via compatible CV controllers.
Voltage Drop Sensitivity: Prone to brightness inconsistencies in long runs (>5m) without thickened wires.
Advantages: Cost-effective, Ease of Installation, and Short-Distance Efficiency.
(2) Constant Current LED Strips
Definition: A Constant Current (CC) LED Strip is a lighting solution engineered to maintain a fixed output current while allowing voltage to fluctuate dynamically based on the load.
Features:
Current Range: Matched to the power supply.
LED Configuration: LEDs arranged in parallel or hybrid series-parallel circuits to ensure uniform current distribution.
Dimming Compatibility: Supports both PWM and linear dimming via CC controllers.
Voltage Drop Tolerance: Unaffected by voltage drop in long runs (>10m) due to adaptive voltage regulation.
Advantages: Uniform Brightness, Thermal Efficiency, and Flexible Voltage Input.
3.7 Classification by SMD Led Size:
3014, 5730, 2216, 5050, 2835, 3528, 2110, 3528, 335 and so on.
3.8 Classification by Direction of Light Emission:
(1) Edge-Lit LED Strip:
Emission Direction: Light Emit from the side or edge of led strip
Technology:LEDs are mounted along the edge
Advantages: High concealment, ideal for indirect lighting in cabinets, gaps, or architectural niches.
Applications: Under-cabinet lighting, TV backdrop slots, stair tread edges.
(2) Font-Lit LED Strip:
Emission Direction: Light projects forward from the strip’s exposed surface.
Technology:
LEDs face upward/forward, with optional lenses/diffusers to control beam angles.
Advantages: High brightness for direct lighting/decoration.
Applications: Ceiling coves, headboard backdrops, retail displays.
(3) Multi-Directional LED Strip:
Emission Direction: Combines multiple directions.
Technology:
LEDs are arranged on both sides or angles, leveraging reflective structures for 3D effects.
Advantages: Layered lighting for complex spaces.
Applications: Floating ceilings, art installations, automotive interiors.
(4) Adjustable LED Strip:
Emission Direction: Mechanically or modularly adjustable angles.
Technology:
LEDs mounted on swiveling brackets or segmented control systems.
Smart variants allow remote angle adjustment.
Advantages: Dynamic adaptability for changing needs.
Applications: Conference rooms, stage setups, customizable home decor.
(5) Specialized Emission Forms LED Strip:
COB Integrated Strips: Uniform, gap-free front-lit illumination.
S shape Bendable Flexible Strips: Bendable for curved surfaces with multi-angle emission.
3.9 Classification by Working Principle:
(1) Analog LED Strip:
Definition: An Analog LED Strip is a lighting product controlled by continuous voltage or current signals (analog control) rather than digital protocols like PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). It offers basic brightness and color adjustment capabilities without advanced dynamic effects.
Features:
Color Capability: Monochromatic (single-color) or limited Dual – Color Temperature options.
Dynamic Effects: Unsupported; limited to static or gradual brightness changes.
Compatibility: Works with analog dimmers
Voltage Range: Typically 12V/24V DC, matching standard analog power supplies.
Advantages: Cost-effective, Smooth Dimming and Reliability.
(2) Digital LED Strip:
Definition: A Digital LED Strip is an advanced lighting solution controlled by discrete digital signals, enabling precise dynamic effects, color customization, and smart integration.
Features:
Color Capability: Supports 16 million colors (RGB/RGBWW) with precise white temperature tuning.
Dynamic Effects: Enables animations (chasing, fading, music sync) via microcontroller programming.
Smart Integration: Works with smart home systems (Wi-Fi/Bluetooth) for voice/remote control.
Voltage Range: Typically 12V/24V DC, requiring compatible digital drivers.
Advantages: Enhanced Functionality, Precision Control, and Scalability.
3.10 Classification by Cuttable Length:
(1) Fixed-Cuttable LED Strip: Pre-engineered with marked intervals (e.g., every 5 cm or 10 cm) where they can be safely cut. Cutting outside these points risks damage to the circuit or LEDs. It includes a standard fixed-cuttable led strip (Cutting Interval ≤5–10cm) and a Mini Cuttable LED Strip (Cutting Interval ≤2.5cm).
Features:
Circuit Structure:
Segmented design with parallel/series connections between marked points.
Each segment operates independently after cutting.
Voltage Stability:
Requires proper termination (e.g., soldering or connectors) to maintain electrical continuity.
Applications: Linear installations and environments need precise, uniform lengths.
(2) Arbitrary-Cuttable LED Strips
Definition:
It can be cut at any position without pre-defined markers, offering maximum flexibility.
Features:
Circuit Design:
Uses redundant traces or flexible PCB layouts to ensure continuity after cutting.
May incorporate surface-mount technology (SMT) for compact, repairable connections.
Termination Options:
Often paired with adhesive-backed connectors or solderless clips for easy reconnection.
Applications: Irregular spaces and Prototyping or DIY projects requiring custom shapes.
(3) Non-Cuttable LED Strips
Definition:
Permanently sealed or integrated into fixtures, unable to be shortened.
Features:
Construction:
Encased in waterproof tubing (e.g., silicone) or embedded in rigid materials.
Pre-wired to specific lengths for fixed installations.
Application: Outdoor lighting and OEM applications.
4. LED Strip Features
(1) High Brightness & Energy Efficiency
(2) Extended Operational Lifespan & Reliability
(3) Miniaturization & Flexibility
(4) Accurate Color & Light Control
(5) Safety & Environmental Compliance
(6) Modular & Smart Integration
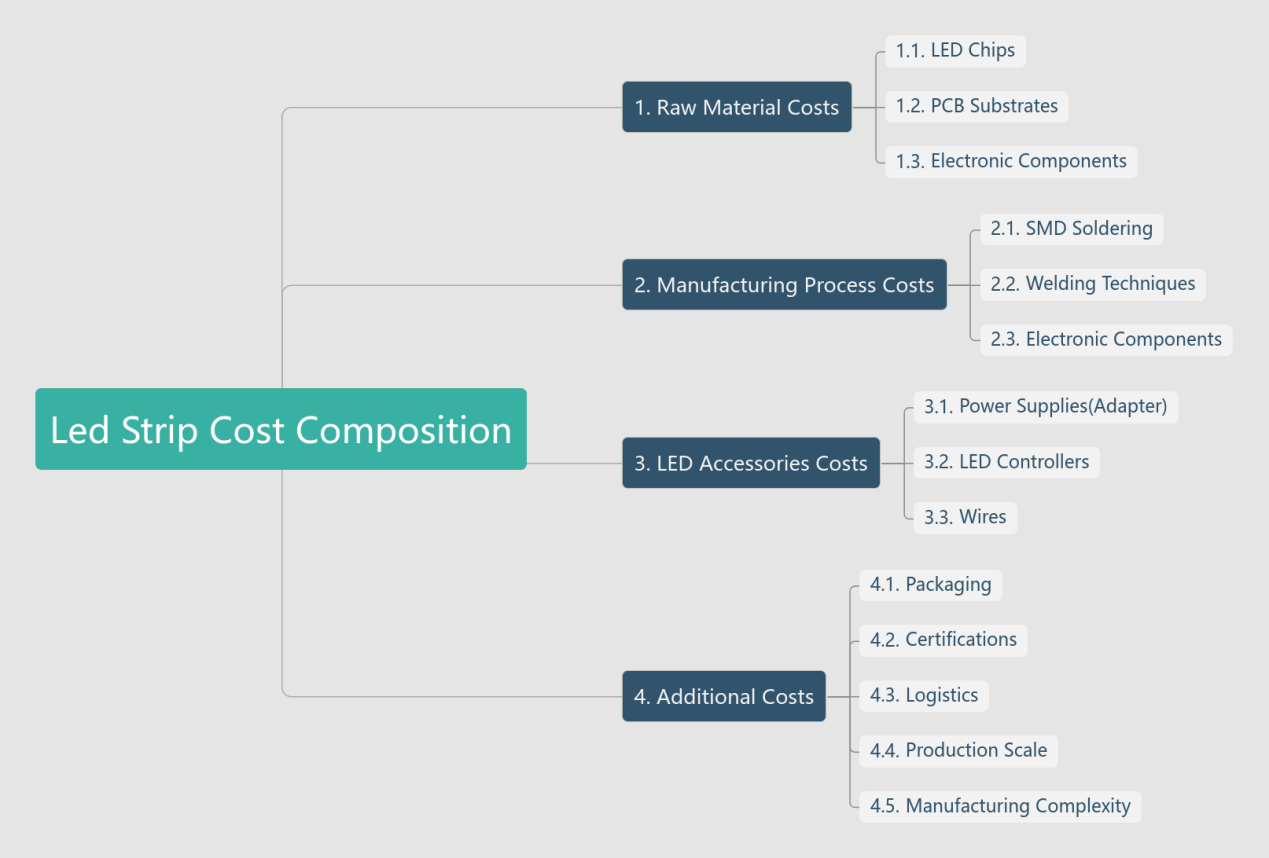
5.Led Strip Cost Composition
(1) Raw Material Costs (40%–60%)
LED Chips: Determine brightness, color temperature, and lifespan.
PCB Substrates: flexible PCB or Rigid PCB(FR4 or Aluminum PCB)
Electronic Components: Resistors, capacitors, and IC drivers.
(2) Manufacturing Process Costs (20%–30%)
SMD Soldering: Costs include high-speed pick-and-place machine depreciation and solder paste.
Welding Techniques: Automated lines are cheaper than manual soldering (¥0.05 per joint).
Encapsulation Processes: Potting (IP65) or sleeve-based waterproofing or ….
(3) LED Accessories Costs
Power Supplies(Adapter): 5V/12V/24V/36V LED Power supply(Adapter)
LED Controllers:Analog PWM dimmers or Digital DMX512 controllers or Smart WiFi modules
Wires: 2 Pins or 3 Pin or 4 Pins or 5 Pins Wires.
(4) Additional Costs
Packaging: Reel packaging is 10%–15% more expensive than bulk packaging.
Certifications: CE/UL approvals cost.
Logistics: International sea freight averages USD80–150 per cubic meter.
Production Scale:
Small-Batch Customization (<500m): Unit cost +30–50%
Mass Production (>10,000m): Cost reduction of 20–30% (bulk pricing, automated assembly).
Manufacturing Complexity:
Hand Soldering: USD0.08–0.15/m
SMT + Reflow: USD0.03–0.07/m
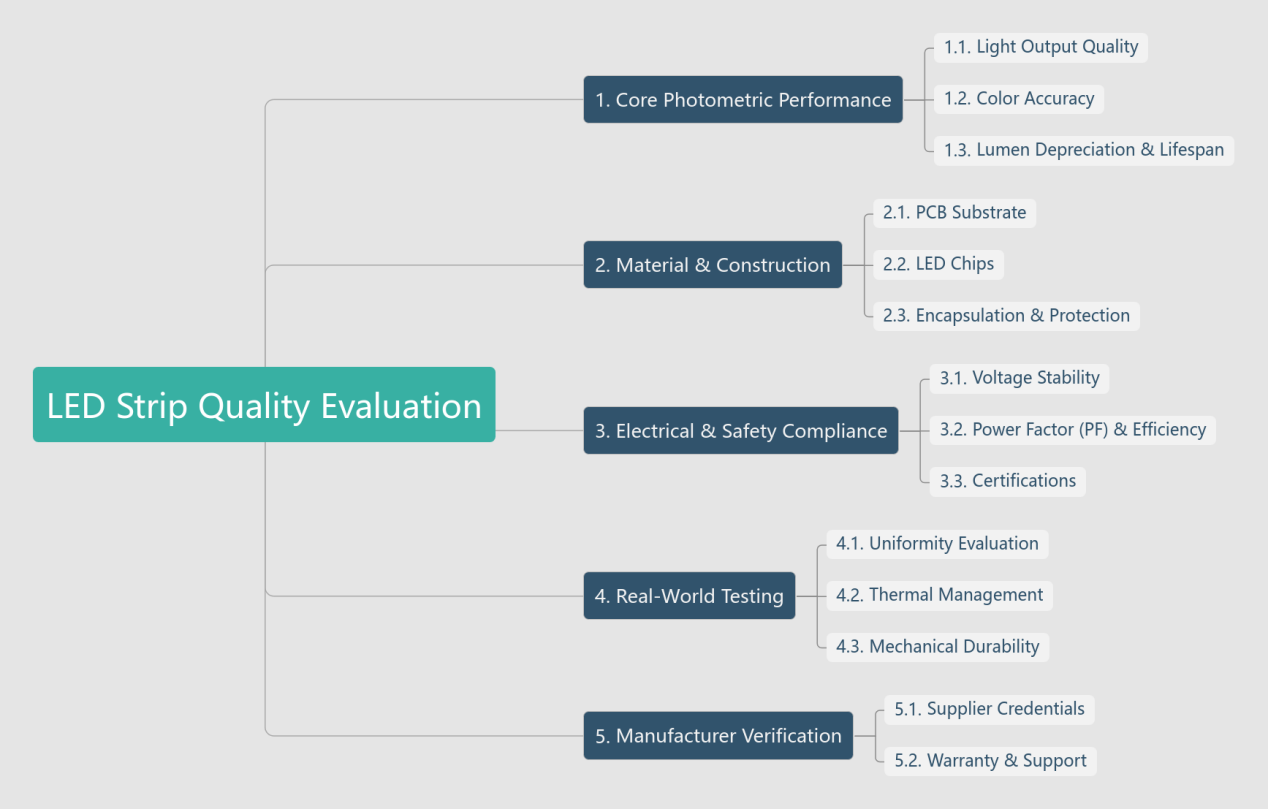
6. LED Strip Quality Evaluation
6.1 Core Photometric Performance
(1) Light Output Quality
Luminous Flux (Lumens/meter): Measure using an integrating sphere or lux meter; deviation from claimed values should be <10%.
Color Temperature Consistency (ΔCCT): Use a chroma meter to verify uniformity; high-quality strips exhibit ΔCCT <±50K.
Color Rendering Index (CRI/Ra):
Validate via spectrometer: ≥80 for commercial use, ≥95 for critical applications (museums, photography).
(2) Color Accuracy (RGB/RGBW Models)
Gamut Coverage: >90% NTSC/Adobe RGB for premium RGB strips.
White Light Purity: RGBW strips in white mode should maintain ΔCCT <3% from nominal values.
(3) Lumen Depreciation & Lifespan
LM-80 Reports: Verify LED chip data.
Empirical Testing: Luminous flux decline <5% after 72 hours of continuous operation.
6.2 Material & Construction
(1) PCB Substrate
Material:
Standard: Flexible FR4 (fiberglass) or PET.
High-power: Metal-core PCB (MCPCB, thermal conductivity ≥2.2 W/m·K).
Copper Thickness:
≥2 oz (68 μm) for current handling; inferior strips use 1 oz copper, risking overheating.
(2) LED Chips
Encapsulation:
Microscope inspection for uniform phosphor coating (eliminate color shifts).
Material:
Alloys/Pure Gold(Pure Gold is better).
Lead Frames:
Copper/Iron(copper is superior to iron, and pure copper offers superior conductivity and durability compared to copper-zinc alloy).
Width:
Thicker is better.
(3) Encapsulation & Protection
IP Rating:
IP65: Silicone conformal coating (splash-resistant).
IP68: Fully potted tubing (submersion-proof for 30 minutes).
Solder Joints:
Reflow-soldered joints must withstand >5N shear force.
6.3 Electrical & Safety Compliance
(1) Voltage Stability
Voltage Drop Test:
<0.5V drop over 5m (12V systems) or <1V (24V systems).
(2) Power Factor (PF) & Efficiency
PF: >0.9 for premium drivers; low PF (<0.5) causes grid harmonics.
System Efficacy: >80 lm/W.
(3) Certifications
Safety: UL 2108 (North America), EN 60598 (EU), GB 7000 (China).
Environmental: RoHS (lead-free), REACH (hazardous substance-free).
6.4 Real-World Testing
(1) Uniformity Evaluation: Visual Inspection and Grayscale Gradient.
(2) Thermal Management
Temperature Rise:
Infrared thermography at 25°C ambient:
Low power (<10W/m): Rise <15°C.
High power (>20W/m): Rise <30°C (requires aluminum channels).
(3) Mechanical Durability
Flex Test: Wrap around a 50mm cylinder 10 times; no open circuits or brightness loss.
Adhesion Test: 3M VHB tape must sustain a 1kg load for 24 hours without detachment.
6.5 Manufacturer Verification
(1) Supplier Credentials
(2) Warranty & Support
Coverage:
Consumer grade: 1–2 years.
Professional grade: 3–5 years.
Technical Support: Availability of IES/Dialux files, and custom driver solutions.
7. How to Select the Right LED Strip
(1) Requirement Analysis: Define functional purpose (Primary Lighting, Ambient Decoration, or Specialized Applications), environmental conditions (Indoor/Dry Areas, Kitchens/Bathrooms, or Outdoor/Submersible), and control needs (Basic, Smart Integration or Advanced Programming).
(2) Parameter Matching: Select suitable types according to brightness, CCT, voltage, and length.
(3) Validation: Test samples for color uniformity, compatibility, and thermal performance.
8. How to Power LED Strips
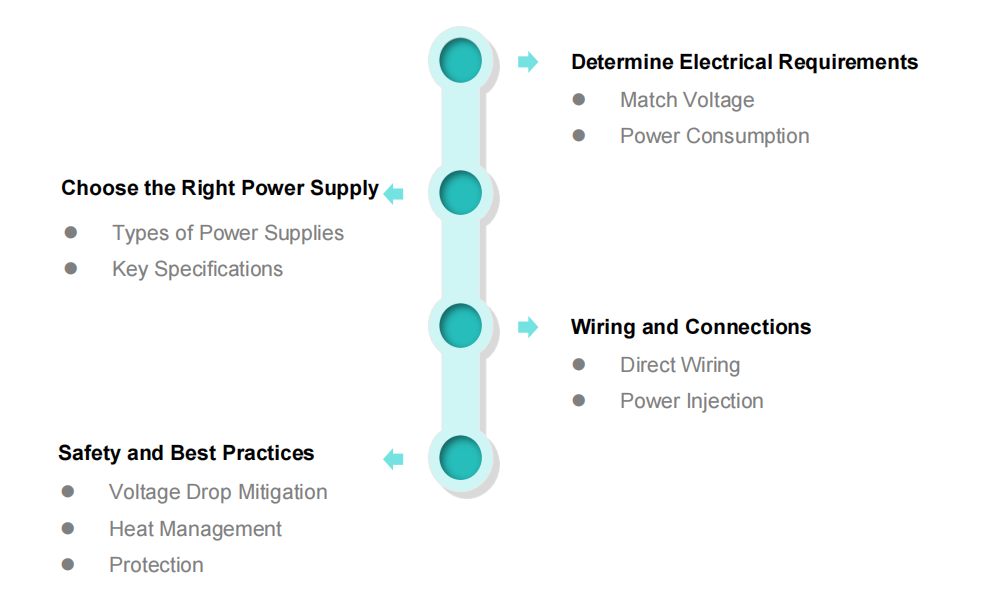
Powering LED strips correctly ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety.
8.1 Determine Electrical Requirements
(1) Match Voltage: 5V, 12V, or 24V DC. Check the strip’s label or datasheet.
(2) Power Consumption
Calculate total wattage: Length (meters) × Power per Meter (W/m).
Select a power supply with 20–30% headroom.
8.2 Choose the Right Power Supply
(1) Types of Power Supplies
Plug-in Adapters: For indoor/short runs.
Switching Power Supplies: For high-power/long runs.
Dimmable Drivers: For strips with brightness control.
Waterproof PSUs: IP67-rated for outdoor/wet environments.
(2) Key Specifications
Output Voltage: This must match the strip’s voltage.
Current Rating: Ensure the PSU’s max current (A) exceeds the strip’s total current.
8.3 Wiring and Connections
(1) Direct Wiring
Strip Terminals: Use soldering or JST/SM connectors for secure joints.
Multiple Strips: Wire in parallel (not series) to avoid voltage drop.
(2) Power Injection
For long runs (>5m), add additional power feeds at intervals to prevent dimming.
8.4 Safety and Best Practices
(1) Voltage Drop Mitigation
Use thicker wires for long connections.
Opt for higher voltage (24V) strips for long installations.
(2) Heat Management
Avoid enclosing high-power strips (>15W/m) without thermal dissipation.
(3) Protection
Add a fuse between the PSU and the strip.
Use waterproof seals for outdoor installations.
9. How to Connect LED Strip
(1) Match the voltage between the strip and the power supply.
(2) Cut carefully at designated points.
(3) Secure connections with soldering or clip connectors.
(4) Test and reinforce long runs with power injection.
(5) Prioritize safety with proper insulation and heat management.
10. LED Strip Installation & Maintenance
10.1 Pre-Installation
(1) Surface Prep: Clean with alcohol, and apply 3M primer for adhesive bonding.
(2) Power Planning:
12V strips: Reinject power every 5m; 24V strips extend to 10m.
Use parallel connections for multi-segment runs.
(3) Thermal Management:
Mandatory aluminum channels for >10W/m strips.
Avoid enclosed spaces.
10.2 Controller Options
(1) Basic: RF remotes (range <10m).
(2) Smart: HomeKit/Alexa-compatible.
(3) Pro: DMX512 controllers.
10.3 Troubleshooting
(1) Dimming at Ends: Voltage drop → Shorten runs or add power injection.
(2) Color Inaccuracy: Verify controller protocol (SPI vs. PWM).
(3) Dead Sections: Broken solder joints → Repair with conductive adhesive.
11. LED Strip Applications
(1) Architecture & Interior Design: Architectural Contour Lighting, Ambient Indoor Lighting, Commercial Spaces.
(2) Retail & Display: Product Highlighting, Signage & Advertising, Hospitality Lighting.
(3) Residential & Smart Homes: Functional Lighting, Decorative Accents, Smart Integration: Wi-Fi/Bluetooth connectivity (e.g., Philips Hue) for voice control and scene automation.
(4) Automotive & Transportation: Interior Ambient Lighting, Exterior Styling, Traffic Guidance.
(5) Entertainment & Media Production: Stage Lighting, Film/Photo Lighting, Theme Parks.
(6) Industrial & Warehousing: Task Lighting, Safety Indicators, Equipment Status.
(7) Healthcare & Wellness: Surgical Lighting, Phototherapy, Healing Environments.
(8) Agriculture & Vertical Farming: Plant Growth Lighting, Vertical Farms, Aquaculture.
(9) Public Infrastructure & Urban Lighting: Smart Streetlights, Transit Guidance, Energy Retrofits.
(10) Art & Creative Installations: Interactive Art, Kinetic Sculptures, Fashion Tech.
12. LED Strip Best Manufacturers
There are plenty of LED strip brands in the world, below is a list of some of the famous manufacturers.
Philips
Cree Lighting
Osram
Nichia
Panasonic
Simon
Unilumin
Refond
Opple
RISHANG
…
Besides the above manufacturers, you can also choose Y&T Technology Development Co.,Ltd.
Our company is a professional manufacturer of led strip for more than 11 years, with high quality, fast delivery, and competitive price. Our products are backed by a three-year limited warranty. For technical support or customization requests, please contact us.
13. LED Strip FAQs
14. Summary
The applications of LED strips have extended beyond traditional lighting scenarios to cutting-edge fields such as smart IoT, industrial manufacturing, and life sciences. Moreover, their technological boundaries continue to expand alongside advancements in materials science and artificial intelligence. Looking ahead, breakthroughs in flexible displays and energy storage technologies are poised to transform LED strips into critical interfaces connecting the physical and digital worlds.